Content

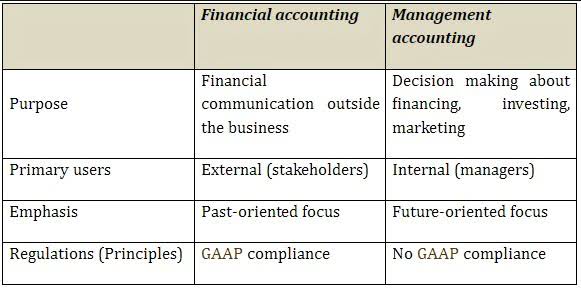
Balance SheetA balance sheet is one of the financial statements of a company that presents the shareholders’ equity, liabilities, and assets of the company at a specific point in time. It is based on the accounting equation that states that the sum of the total liabilities and the owner’s capital equals the total assets of the company. Cash And Cash EquivalentsCash and Cash Equivalents are assets that are short-term and highly liquid investments that can be readily converted into cash and have a low risk of price fluctuation. Cash and paper money, US Treasury bills, undeposited receipts, and Money Market funds are its examples. They are normally found as a line item on the top of the balance sheet asset.
- The 2022 projected ratio is 0.18, which is below 0.20, indicating that some farms may be having difficulty repaying loans.
- In addition to business licenses and permits, some practitioners require annual licensing or continuing education.
- In any case, negative working capital is always a sign of a company whose finances are not doing well, but not necessarily to the extent it is going bankrupt.
- Small businesses need to keep a certain level of inventory to sustain operations and meet customer demand.
A current ratio of 1.5 to 2.0 is sometimes believed to be ideal, although an ideal Working Capital Ratio can vary between industries. Businesses that have a working capital ratio of less than one have a negative cash flow. There are a number of metrics companies can use to help prevent these problems and the current ratio is one of them. Discover why Balmain, a French fashion couture brand founded in 1945, chose our services to protect its receivables as part of its B2B operations.
Working Capital Ratio Calculator
In contrast, capital-intensive companies that manufacture heavy equipment and machinery usually can’t raise cash quickly, as they sell their products on a long-term payment basis. If they can’t sell fast enough, cash won’t be available immediately during tough financial times, so having adequate working capital is essential. Current liabilities are the amount of money a company owes, such as accounts payable, short-term loans, and accrued expenses, that are due for payment within a year. Current assets, such as cash and equivalents, inventory, accounts receivable, and marketable securities, are resources a company owns that can be used up or converted into cash within a year.
- This in turn may discourage other suppliers from extending credit to the company.
- Dell’s negative CCC is a result of the very low levels of inventory and the rather long time Dell takes to pay its creditors.
- The turnover ratio portrays the efficiency at which a company’s operations can create sales, which supports the statement from earlier about net working capital being preferable over working capital.
- In general, the current ratio of less than 1 might suggest potential liquidity issues, whilst the current ratio of 1.2 to 2 is regarded as desirable.
- The current ratio helps business owners answer exactly these questions—hopefully before they find themselves in a cash flow pinch.
- Working capital changes from year to year can be estimated using working capital as a percentage of revenues.
Like most other financial ratios, net working capital ratio also cannot justify the exact financial condition of a company alone. For best guesses, one must consider other financial ratios and compare the chosen company’s ratios with other companies’ values in the same industry. When a company has excess current assets, that amount can then be used to spend on its day-to-day operations. Working capital is equal to current assets minus current liabilities. The working capital ratio is a metric that reflects a company’s ability to pay off its debts with its assets. Avoid financing fixed assets with working capital, such as IT equipment. Lease or take out a long-term loan instead of depleting your company’s cash.
How Is The Working Capital Ratio Calculated?
Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate.
Meanwhile, a negative NWC means current liabilities exceed current assets. Current liabilities are short-term financial obligations due within one year. Current liabilities usually include short-term loans, lines of credit, accounts payable (A/P), accrued liabilities, and other debts, such as credit cards, trade debts, and vendor notes. The sum of monthly payments of long-term debt―like commercial real estate loans and small business loans―that will be made within the next year are also considered current liabilities.
In other words, will I have enough cash to pay my vendors when the time comes? And if not, can I liquidate some things to help cover the difference? The current ratio helps business owners answer exactly these questions—hopefully before they find themselves in a cash flow pinch.
Working Capital Vs Current Ratio
To spot an extremely high turnover ratio, you need to compare the ratio for your company with other businesses in the same industry and scale. The working capital turnover is the ratio that helps to measure a company’s efficiency in using its working capital to support sales.
A working capital ratio that continues to decline is a major cause of concern and a red flag for financial analysts. Alternatively, they may consider the quick ratio which is used to indicate short-term liquidity because it includes account receivables, cash, cash equivalents, and marketable investments. The current ratio is the ratio that identifies the availability of current assets to cover current liabilities. Income taxes payable, payroll taxes payable, short-term loans, and accounts payable are examples of current liabilities. Working capital is the difference between current assets and current liabilities, while the net working capital calculation compares current assets and current liabilities.
1 5 The Balance Sheet
Should the business fail to increase its working capital or if its cash flow decreases further, it could face serious financial difficulties. A business’s working capital ratio can show how efficient its operations are along with how healthy its short-term finances are. A working capital ratio of 1 indicates that a company will have to sell all its assets to be able to pay its debt.

The faster the assets can be converted into cash, the more likely the company will have the cash in time to pay its debts. When a working capital calculation is positive, this means the company’s current assets are greater than its current liabilities. The company has more than enough resources to cover its short-term debt, and there is residual cash should all current assets be liquidated to pay this debt. Insert current assets and current liabilities totals from your most recent balance sheet to calculate the current ratio. Your current assets and liabilities can assess operational efficiency and liquidity. They form part of your working capital as they affect the core operations. That is why working capital management is integral to sound cash flow management.
Therefore, the high working-capital ratio would mask underlying liquidity problems. Cash includes bank deposits, certificates of deposit and short-term Treasury bills.
What Do Liquidity Ratios Measure?
A high working capital ratio indicates that a company has more ability to pay its current liabilities and is less risky to creditors and investors. In addition, the working capital ratio is one of the many metrics that can be used to assess a company’s potential for insolvency. In any case, negative working capital is always a sign of a company whose finances are not doing well, but not necessarily to the extent it is going bankrupt.
Current assets are assets that a business expects to use in the near future. To better explain inventory to working capital,it is an important indicator of a company’s operation efficiency. Note that a low value of 1 or less of inventory to working capital means that a company has high liquidity of current asset. While it may also mean insufficient inventories, high value inventory to working capital ratio means that a company is carrying too much inventory in stock. Because excessive inventories can place a heavy burden on the cash resources of a company, it is not favorable for management. A key issue for a company to improve its operation efficiency is to identify the optimum inventory levels and thus minimize the cost tied up in inventories.
Working capital becomes negative when the nondebt current liabilities exceed noncash current assets. Negative noncash working capital is considered as a source of default risk for a firm. In long run, change in cash flow has to be assumed to be zero or positive in the long run. Working capital is the measure of the liquidity available https://www.bookstime.com/ in a company with which the company funds its daily operations. Working capital is also called net working capital, it is the amount of liquidity left for a company after its current liabilities have been removed from the current assets. The formula for calculating working capital is (Current Assets – Current Liabilities).
Adjustments To The Working Capital Formula
Yes, it is bad if a company’s current liabilities balance exceeds its current asset balance. This means the company does not have enough resources in the short-term to pay off its debts, and it must get creative on finding a way to make sure it can pay its short-term bills on time. Companies can forecast what their working capital will look like in the future.

Working capital management demands coordinated actions and strategies for optimal inventory and accounts receivables as one part of the company’s liquidity. For instance, even if a company has a net working capital of 1.8, it can still have a slow inventory turnover or slow collection of receivables. Both potential issues can lead to delays in the availability of actual liquid assets. Because this ratio measures assets as a portion of liabilities, a higher ratio is better for companies, investors and creditors. It means the firm would have to dispose of all current assets before it can pay off its current liabilities. It is important to note that the current assets and current liabilities are placed firstly, which is then followed by long-term assets and liabilities.
Tracking Various Ratios
This way, investors and creditors get a hold of the financial status of any company. The rapid increase in the amount of current assets indicates that the retail chain has probably gone through a fast expansion over the past few years and added both receivables and inventory. The sudden jump in current liabilities in the last year is particularly disturbing, and is indicative of the company suddenly being unable to pay its accounts payable, which have correspondingly ballooned. The acquirer elects to greatly reduce her offer for the company, in light of the likely prospect of an additional cash infusion in order to pay off any overdue payables.
Working capital is the amount whereas the current ratio is the proportion or quotient available of current assets to pay off current liabilities. In addition to this, the current ratio is important with respect to the investors’ point of view. The current ratio gives a quick grasp over the liquidity position of a company to investors. Whereas working capital is important with respect to the owner’s point of view. Because working capital tells the financial stability of a company and helps to fulfill short-term goals. It proves the company isn’t operating efficiently, meaning, it cannot settle its obligations properly.
Though the company may have positive working capital, its financial health depends on whether its customers will pay and whether the business can come up with short-term cash. Current assets listed include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and other assets that are expected to be liquidated or turned into cash in less than one year.